Are you looking for investment, pitch your idea with us!
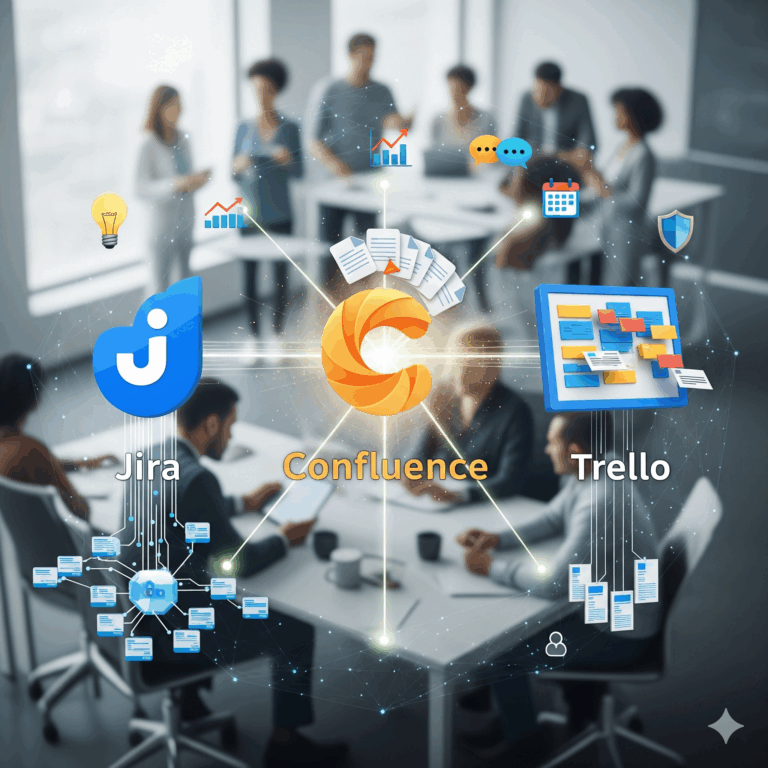
In today’s digital-first world, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) has become the backbone of modern business operations. From project management and customer relationship management (CRM) to cloud storage and AI-powered analytics, SaaS solutions enable companies to operate with agility and scalability. However, as adoption increases, so does the risk of cyber threats. By 2025, the conversation around SaaS is no longer about convenience or cost savings—it’s about security.
This article explores why SaaS security matters more than ever in 2025, the most pressing cyber threats businesses face, and the strategies companies can adopt to safeguard their operations.
Why SaaS Security Matters in 2025?
The SaaS industry is expected to cross $1 trillion in market value by 2030, and businesses of all sizes—from startups to enterprises—are embracing it. However, with greater reliance on cloud-based systems comes greater exposure to risks such as data breaches, insider threats, and ransomware attacks.
The rise of remote and hybrid work models has also expanded the attack surface. Employees access SaaS platforms from multiple devices and networks, making it harder to enforce consistent security protocols. Furthermore, cybercriminals are evolving, leveraging AI to create sophisticated phishing attacks and malware that target SaaS platforms directly.
Top Cyber Threats Facing SaaS Platforms in 2025
1. Data Breaches
SaaS applications often store sensitive customer and business data. A single breach can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory fines. Attackers exploit misconfigured cloud settings or weak access controls to gain entry.
2. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Ransomware attacks have become more organized. With “RaaS,” even non-technical attackers can rent ransomware tools on the dark web. SaaS platforms are prime targets because they store critical operational data that companies cannot afford to lose.
3. Insider Threats
Not all risks come from outside. Disgruntled employees or careless users can expose company data. In some cases, attackers trick insiders into sharing login details through social engineering attacks.
4. API Exploits
Modern SaaS platforms rely heavily on APIs to integrate with other services. However, insecure APIs can be exploited by hackers to manipulate data or bypass authentication systems.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Risks
With stricter laws like the GDPR in Europe and DPDP Act in India, businesses face penalties if customer data isn’t adequately protected. SaaS providers that fail to comply with evolving regulations can put their clients at legal risk.
Best Practices to Strengthen SaaS Security
1. Zero Trust Security Model
In 2025, businesses are adopting Zero Trust, which assumes that no user or device is inherently trustworthy. Every login and transaction is verified continuously, minimizing the chance of unauthorized access.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Relying on passwords alone is outdated. MFA—using biometrics, OTPs, or hardware tokens—adds an extra layer of defense, making it harder for hackers to break in even if credentials are compromised.
3. Data Encryption
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit ensures that even if attackers intercept information, it remains unreadable. End-to-end encryption is becoming a non-negotiable standard in SaaS platforms.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
AI-powered monitoring tools help businesses identify unusual behavior in real-time. For instance, if a user logs in from two different continents within minutes, the system can automatically flag or block the attempt.
5. Vendor Risk Management
Companies must evaluate the security posture of their SaaS providers. This includes reviewing certifications (like ISO 27001, SOC 2) and ensuring that providers follow best practices for data protection.
6. Regular Security Training
Employees remain the weakest link in cybersecurity. Regular training sessions can teach staff how to spot phishing emails, use strong passwords, and follow company security policies.
7. Backup and Recovery Plans
Even with strong defenses, no system is 100% breach-proof. Regular backups and disaster recovery strategies ensure businesses can quickly bounce back from an attack without paying ransoms.
The Role of AI in SaaS Security
Interestingly, the same AI technology that cybercriminals exploit is also empowering SaaS security teams. AI-driven security tools can:
- Detect anomalies faster than human analysts.
- Automate responses to common attacks.
- Predict vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
By 2025, AI is no longer optional—it’s essential for scaling SaaS security against evolving threats.
Looking Ahead: The Future of SaaS Security
The SaaS ecosystem in 2025 is both opportunity-rich and risk-heavy. Businesses that treat security as an afterthought risk losing customer trust and facing regulatory consequences. On the other hand, companies that proactively invest in cybersecurity can turn it into a competitive advantage.
Expect SaaS security to become a selling point, with providers highlighting their encryption methods, compliance certifications, and AI-powered defense systems as part of their value proposition. Customers will increasingly choose vendors not just for features, but for trustworthiness.
Conclusion
As SaaS continues to dominate the digital landscape in 2025, cybersecurity has become the foundation of trust between providers and businesses. The threats are real—ranging from data breaches to ransomware—but the solutions are equally powerful. By adopting best practices such as Zero Trust, encryption, AI-driven monitoring, and strong compliance measures, businesses can stay ahead of attackers.
In the end, SaaS security is no longer just about protecting data—it’s about ensuring business continuity, maintaining customer trust, and shaping the future of digital transformation.